What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a system in the body that helps keep our other bodily systems in balance. Cannabinoids are compounds that bind to cannabinoid receptors found throughout our bodies. Our bodies naturally produce the cannabinoids Anandamide and 2-AG. Cannabis plants also produce phytocannabinoids that closely resemble the ones in our bodies, which is one reason why cannabis is associated with a wide variety of therapeutic benefits. There are several cannabinoids found in cannabis and they are all slightly different in their molecular structure so they have different effects in the body. The ECS is an important system in the body and it explains why cannabis can help with many different conditions.
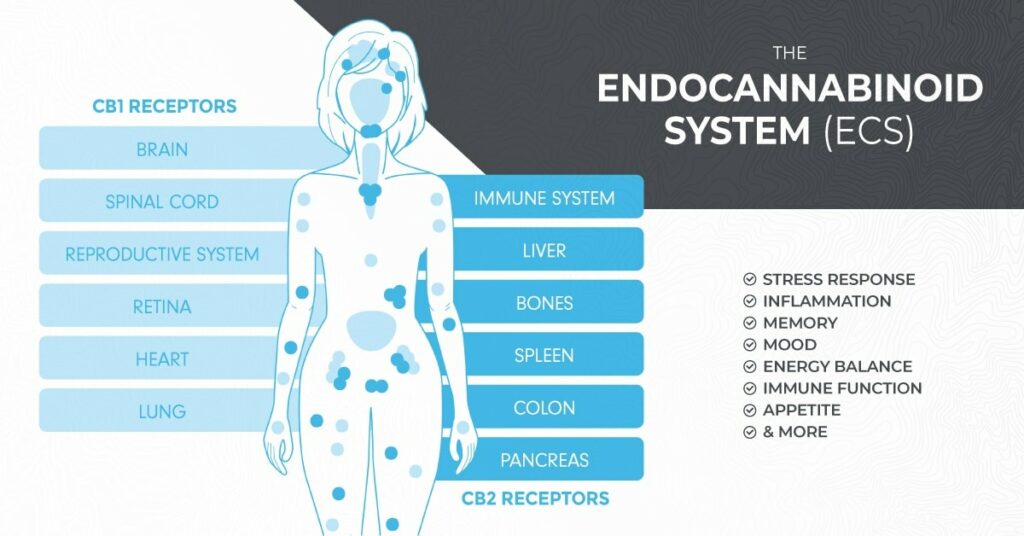
Cannabinoid Receptors
There are two cannabinoid receptors found on cell walls throughout the body, the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Cannabinoids interact with the receptors, much like a lock and key. The receptor is the lock, and the cannabinoid molecule is the key – when the cannabinoid “key” attaches to the receptor “lock,” a reaction is triggered resulting in an effect on the brain and/or body. CB1 receptors are present in the central nervous system, the brain, and in certain peripheral tissues. CB2 receptors are present in peripheral organs and are associated with the immune system and inflammation.
Homeostasis
The ECS works to balance the body to help maintain homeostasis. Homeostasis is the ability to maintain stable conditions inside the body despite fluctuations in the external environment. Illness can occur when the body fails to maintain homeostasis. The ECS helps maintain homeostasis by regulating a variety of functions, including the following:
- Appetite
- Cardiovascular Activity
- Digestion
- Energy
- Immune Function
- Inflammatory Reactions
- Inhibition of Tumor Cells
- Hormonal Activity
- Maintenance of Bone Mass
- Memory
- Mood
- Pain Sensation
- Reproduction
- Sleep
Importance of the Endocannabinoid System
The ECS communicates with other systems in the body, which is why therapeutic cannabis can benefit a wide variety of symptoms and conditions. Cannabis helps stimulate the ECS, but there are other ways to stimulate it that do not involve cannabis. For example, one of our bodies’ natural cannabinoids, Anandamide, is found in chocolate, which may explain why chocolate makes people feel good. Another example is that the feeling of “runner’s high” after exercise may be due to an increase in our bodies’ natural cannabinoids and not from endorphins. Our natural cannabinoids can be influenced by what we do with our bodies and what we put into them. Dysfunction in the ECS may be related to several conditions, and cannabinoids from cannabis can help balance the body. In conclusion, understanding the ECS is crucial to understanding why cannabinoids from cannabis have many potential therapeutic uses.
Continue Learning